What Describes the Inflection Point of a Bell Shaped Curve
In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. How would you describe the shape of a normal curve.

Normal Random Variables 2 Of 6 Concepts In Statistics
Exactly half of data points are to the left of the mean and.
. The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. Two peaks is bimodal and so on. Approximately 95 of all the data is within two standard deviations of the mean.
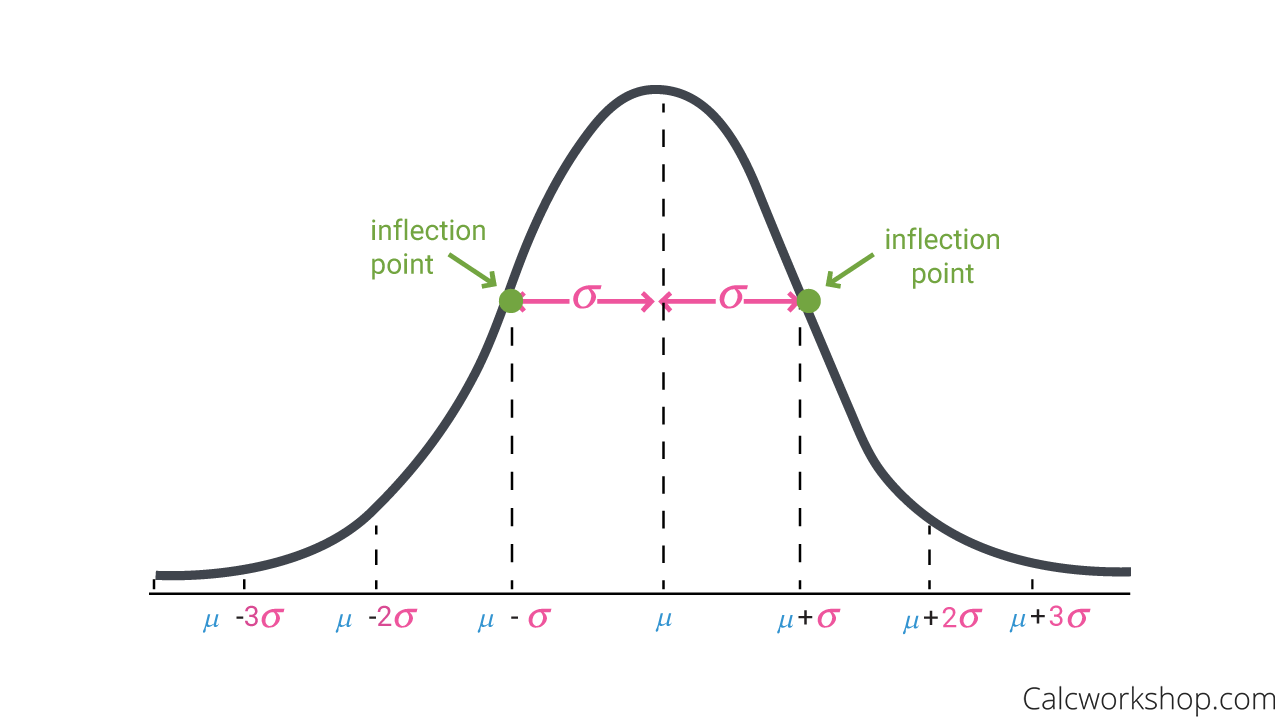
It means that the function changes from concave down to concave up or vice versa. Many measurement variables found in nature follow a predictable pattern. Approximately 68 of all of the data lies within one standard deviation of the mean.
The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean. The predictable pattern of interest is a type of symmetry where much of the distribution of the data is clumped around the center and few observations are found on the extremes. A bell curve has predictable standard deviations that follow the 68 95 997 rule see below.
Changing u without changing q moves the normal. The normal curve is symmetrical about the mean. The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean.
Two points on the curve are of particular interest to us. 2 shows that growth is little abated when external influence is cut off at the tipping point at least for a curve with parameter values p 0025 and q 025. These points in opposite sides of the peak are called the inflection points.
The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. These are the points where the curve changes concavity Explain the 68-95-997 rule. All normal curves are symmetric about the mean mu.
What describes the inflection point of a bell-shaped curve. The point where the curve changes from concave upward to concave downward. Lets take a look at an example of a normal curve and then follow the example with a list of the characteristics of a typical normal curve.
In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean. Mode here means peak.
The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. The curve is symmetrical about the mean. The normal qPCR amplification curve shape.
The curve of the distribution is bell-shaped. The middle curve in Fig. For s-curves in business the inflection point is the point along the curve where changes in the businesss environment or practices shift the curve itself from upward to.
1 all normal curves have the same overall shape. The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. Y 3x 2 12x 12.
In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. Although exact definition of this depends on the instrument software algorithms this is basically the point where the curve first clearly rises off baseline to a statistically significant degree. The curve of the distribution is bell-shaped.
The curve is symmetrical about the mean. A short trail down from the middle peak on either side the bell changes the slope of its curve. A bell curve is symmetric.
One is the CT value. In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. An s-curve describes a curve with an s shape that starts close to zero grows gradually until it reaches a relatively sudden increase then levels off or decreases.
The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean. The proof is left for you as an exercise. The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean.
All normal curves are bell-shaped with points of inflection at mupm sigma. In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. For example the 20 market penetration point is reached only one period later than it would have had advertising continued and the 50 penetration point is reached with three periods delay.
The curve is symmetrical about the mean. The curve of the distribution is bell-shaped. Where on the normal curve are inflection points located.
A bell curve is a graph depicting the normal distribution which has a shape reminiscent of a bell. The distance between the two inflection points of the normal curve is equal to the value of the mean. Approximately 997 of the data is within three standard deviations.
The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. 42 - The Normal Curve. The normal curve of the distribution is bell-shaped.
And 6x 12 is negative up to x 2 positive from there onwards. A bell curve Gaussian distribution has only one mode or peak. The second derivative is.
F x is concave upward from x 2 on. A curve with one peak is unimodal. In other words the point in which the rate of change of slope from increasing to decreasing manner or vice versa is known as an.
Symmetric single-peaked bell-shaped 2 any specific normal curve is completely described by giving its mean u and it standard deviation q 3 the mean is located at the center of the symmetric curve and is the same as the median. Y 6x 12. And the inflection point is at x 2.
The point of inflection or inflection point is a point in which the concavity of the function changes. In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are of equal values. F x is concave downward up to x 2.
The curve is symmetrical about the mean. The top of the curve shows the mean mode and median of the data collected. Data that has this pattern are said to be bell-shaped or have a normal.
The curve of the distribution is bell-shaped. The curve is symmetrical about the mean. This rule states that for a normal curve 68 of the data lies between 1 σ 95 of the data lies.
The normal curve gradually gets closer and closer to 0 on one side. Brase describes the inflection points as the transition points at which the bell curve changes between downward and upward cupping 293. A bell curve follows the 68-95-997 rule which provides a convenient way to carry out estimated calculations.
The curve of the distribution is bell-shaped.

Normal Random Variables 2 Of 6 Concepts In Statistics
No comments for "What Describes the Inflection Point of a Bell Shaped Curve"
Post a Comment